LIMI Study Shows Fewer Training Examples Can Boost AI Agent Performance
A new study suggests that only 78 carefully selected training examples may be sufficient to create superior autonomous AI agents, challenging the need for massive datasets.
A groundbreaking study from Chinese researchers challenges the conventional wisdom in AI development, proposing that just 78 meticulously chosen training examples may be enough to build highly effective autonomous agents. The research, detailed in the LIMI ("Less Is More for Intelligent Agency") paper, redefines AI "agency" as the ability to act independently—identifying problems, forming hypotheses, and solving tasks through self-directed interaction with environments and tools.
Key Findings
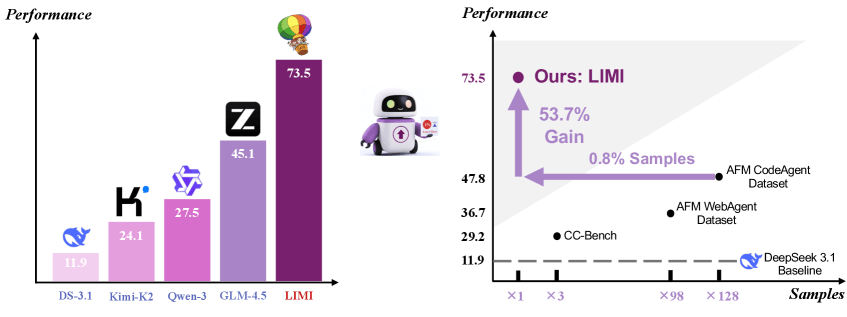
- Performance: On the AgencyBench benchmark, LIMI achieved 73.5% accuracy using only 78 training samples, far outpacing competitors like Deepseek-V3.1 (11.9%), Kimi-K2-Instruct (24.1%), and GLM-4.5 (45.1%).
- Efficiency: LIMI delivered a 53.7% gain over models trained on 10,000 samples, using 128 times less data.
- Success Rate: LIMI nailed 71.7% of requirements on the first try, nearly doubling the best baseline, with an overall success rate of 74.6%.
Methodology
The LIMI team focused on two primary domains:
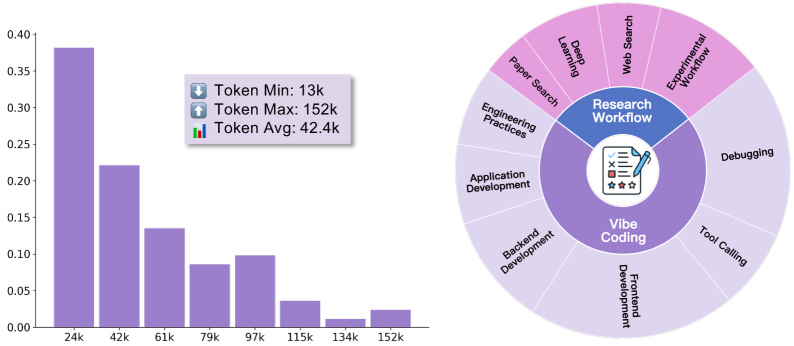
- Collaborative "Vibe Coding": For software development tasks like building C++ chat apps and Java to-do lists.
- Research Workflows: For scientific tasks such as LLM comparisons, data analysis, and sports analytics.
Each training example captured the full process of human-AI teamwork, from initial requests through tool use and problem-solving. Some trajectories extended to 152,000 tokens, showcasing the depth of autonomous behaviors learned.
Implications
The study suggests a paradigm shift in AI training:
- Smaller Models Can Excel: LIMI-Air (106B parameters) improved from 17.0% to 34.3%, while the larger LIMI (355B parameters) jumped from 45.1% to 73.5%.
- Quality Over Quantity: Carefully curated data outperforms massive datasets, aligning with recent findings from Nvidia that smaller models may suffice for agentic tasks.
The code, models, and datasets are publicly available, inviting further research and real-world testing.
Related News
Self-learning AI Agents Transform Enterprise Operations
AI agents trained on their own experiences are revolutionizing operational workflows with emerging practical applications.
SF AI Meetup Explores Next Gen Autonomous Agents and ML
SF AI/ML Meetup on Engineering Next Generation AI Systems with autonomous agents and ML architectures featuring industry leaders.
About the Author

Dr. Sarah Chen
AI Research Expert
A seasoned AI expert with 15 years of research experience, formerly worked at Stanford AI Lab for 8 years, specializing in machine learning and natural language processing. Currently serves as technical advisor for multiple AI companies and regularly contributes AI technology analysis articles to authoritative media like MIT Technology Review.