AI Agents Promise Efficiency But Raise Security and Reliability Concerns
OpenAI and other tech giants are rolling out AI agents to automate tasks like booking flights, but experts warn of security and reliability risks.
OpenAI, along with other major tech players like Google and Perplexity, is pioneering the next evolution of artificial intelligence: AI agents. These virtual assistants are designed to autonomously complete tasks such as booking flights, hotels, or appointments, promising to revolutionize how we interact with the internet. However, experts caution that this technology comes with significant security and reliability risks.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents, like ChatGPT Agent, combine advanced search tools with task automation capabilities. Users interact with them through familiar chatbots, but the agents operate independently, browsing the web and executing tasks on behalf of the user. For example, instead of manually searching for the cheapest flight, an AI agent can do the legwork and present the best options.
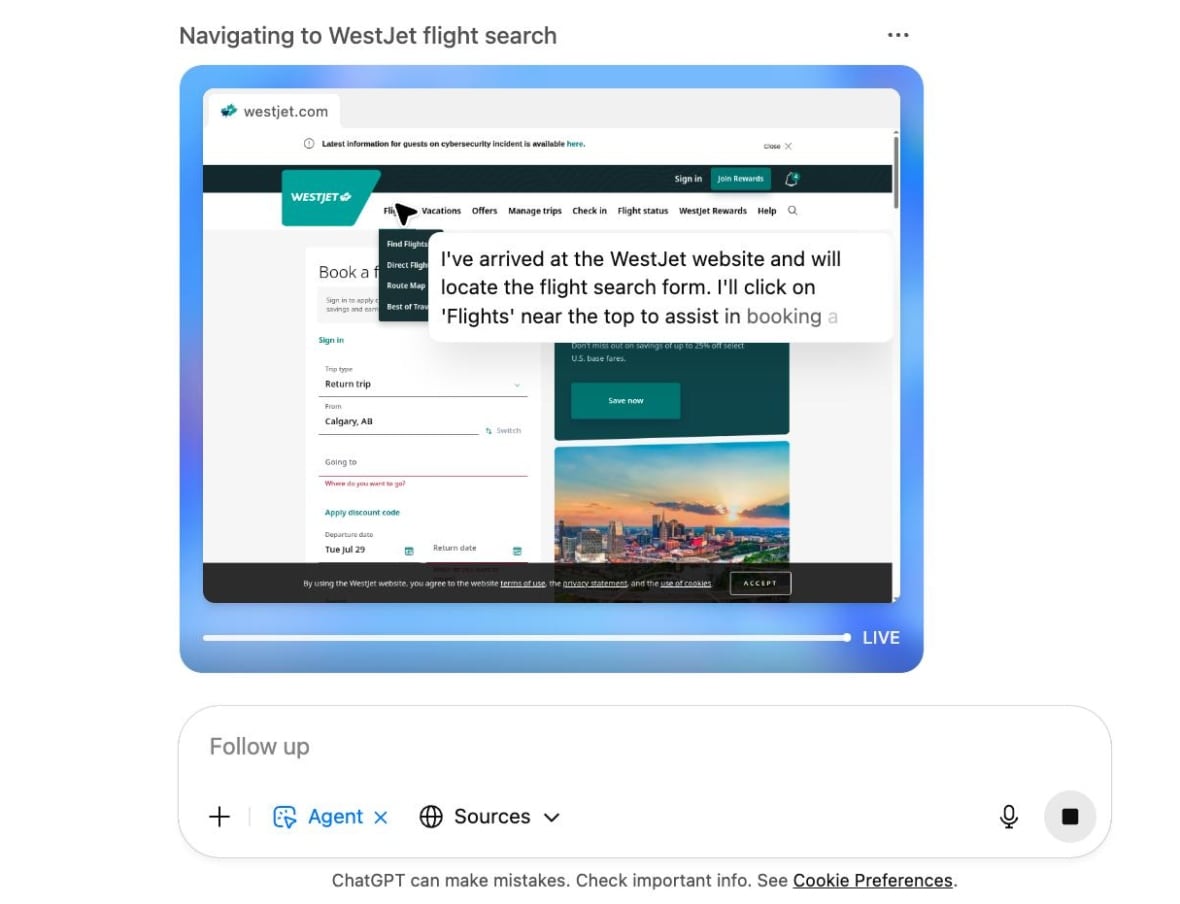
ChatGPT Agent displays text of what it's doing as it carries out the task of booking a flight. (ChatGPT)
The Race to Dominate Agentic AI
The competition to develop the most effective AI agents is fierce. Google is working on Project Mariner, while Perplexity has released Comet Assistant. These tools aim to multitask and learn from user interactions, but their reliability remains a concern.
Gary Marcus, a cognitive scientist and AI entrepreneur, highlights the risks: "Even a tiny slip-up, like booking the wrong nonrefundable ticket, can be costly." AI agents often produce plausible-sounding but inaccurate information, raising questions about their dependability.
Security and Privacy Concerns
For AI agents to be truly useful, they need access to sensitive data like calendars, emails, and credit card information. Meredith Whittaker, president of Signal, warns of "profound issues with security and privacy." OpenAI has introduced safeguards like Takeover mode, which allows users to manually input sensitive data, but vulnerabilities remain.
The Future of Search and Content Creation
AI agents could disrupt traditional search engines like Google. Sinead Bovell, a futurist, notes that current browsers are designed for human traffic, not AI. Pew Research findings suggest that AI summaries reduce website clicks, potentially harming content creators who rely on ad revenue.
Unanswered Questions
Related News
Beginner-Friendly AI Agent Projects to Learn and Build
Explore five practical AI agent projects for beginners, covering scheduling, coding, content creation, research, and search functionalities.
Claude Sonnet 4 5 Advances AI Agents Toward OS Like Capabilities
Anthropic's Claude Sonnet 4.5 coding model demonstrates how AI agents could evolve into dynamic operating systems, raising questions about future app development and security.
About the Author

Dr. Lisa Kim
AI Ethics Researcher
Leading expert in AI ethics and responsible AI development with 13 years of research experience. Former member of Microsoft AI Ethics Committee, now provides consulting for multiple international AI governance organizations. Regularly contributes AI ethics articles to top-tier journals like Nature and Science.