Securing AI-Generated Code with Multiple Self-Learning AI Agents
Read this blog on the research CrowdStrike data scientists have into developing self-learning, multi-agent AI systems that employ Red Teaming capabilities.
CrowdStrike data scientists have developed a self-learning, multi-agent AI system designed to identify and patch vulnerabilities in AI-generated code. The research, presented at the NVIDIA GTC 2025 conference, aims to address the growing cybersecurity risks posed by the rapid adoption of autonomous code generation tools like "vibe coding"—a concept popularized by OpenAI co-founder Andrej Karpathy.
The Challenge: AI-Generated Code and Vulnerabilities
With the rise of large language models (LLMs) enabling non-technical users to generate code via simple prompts, the volume of software—and potential vulnerabilities—is exploding. Traditional human-led vulnerability detection and patching processes struggle to keep pace, creating a widening gap for adversaries to exploit.
The Solution: Three AI Agents Working in Tandem
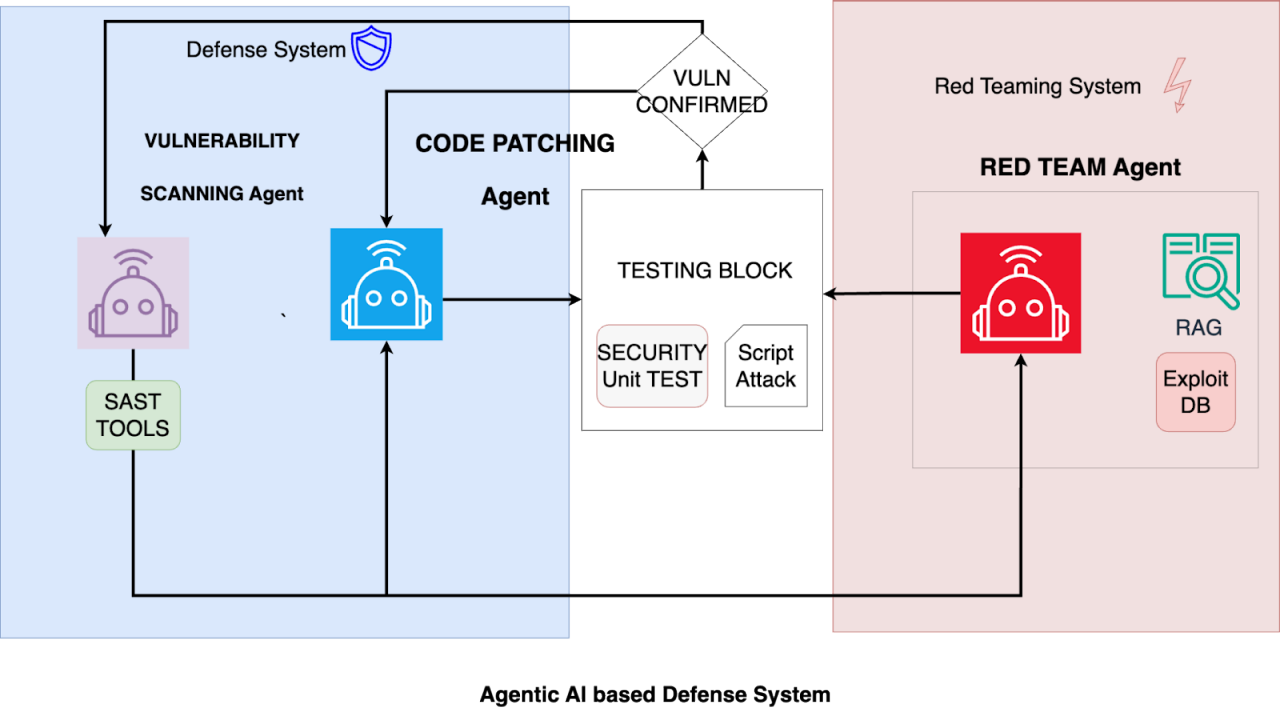
CrowdStrike's proof-of-concept system leverages three specialized AI agents:
- Vulnerability Scanning Agent: Identifies code vulnerabilities using static application security testing (SAST) tools.
- Red Teaming Agent: Builds exploitation scripts to validate vulnerabilities, learning from historical data.
- Patching Agent: Generates security unit tests and patches based on feedback from the other agents.
Key Innovations
- Self-Learning Workflow: Agents continuously improve by sharing knowledge and adapting to new cases.
- 90% Faster Remediation: The system reduces the time to identify and patch vulnerabilities compared to manual processes.
- Proactive Exploitation Testing: The Red Teaming agent simulates real-world attacks to validate vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Industry Implications
CrowdStrike's research highlights the urgent need for AI-native security solutions as autonomous coding becomes mainstream. By integrating security into the development lifecycle, organizations can mitigate risks before code is deployed.
For more details, explore CrowdStrike's Falcon platform or read their blog on .
Related News
AI Agents Fuel Identity Debt Risks Across APAC
Organizations must adopt secure authorization flows for AI environments rather than relying on outdated authentication methods to mitigate identity debt and stay ahead of attackers.
Dynamic Context Firewall Enhances AI Security for MCP
A Dynamic Context Firewall for Model Context Protocol offers adaptive security for AI agent interactions, addressing risks like data exfiltration and malicious tool execution.
About the Author

Dr. Emily Wang
AI Product Strategy Expert
Former Google AI Product Manager with 10 years of experience in AI product development and strategy formulation. Led multiple successful AI products from 0 to 1 development process, now provides product strategy consulting for AI startups while writing AI product analysis articles for various tech media outlets.