The Rise of AI Agents in Modern Business
AI agents are software applications that interact with their environment, gather data, and use it to achieve set goals autonomously or semi-autonomously.
AI agents are transforming the way businesses operate, offering automation, efficiency, and scalability. These software applications interact with their environment, collect data, and use it to achieve predefined objectives. According to a Gartner report, by 2027, nearly 15% of new applications will be automatically generated by AI without human intervention. This shift is expected to flatten organizational structures, with up to 20% of companies eliminating middle management positions by 2026.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
- Autonomy: AI agents operate independently, making decisions without human input.
- Adaptability: They learn from experiences and adapt to new scenarios.
- Goal-Driven: Designed to achieve specific objectives.
- Context Awareness: Understand and respond to the environment they operate in.
- Proactivity: Anticipate needs and take proactive measures.
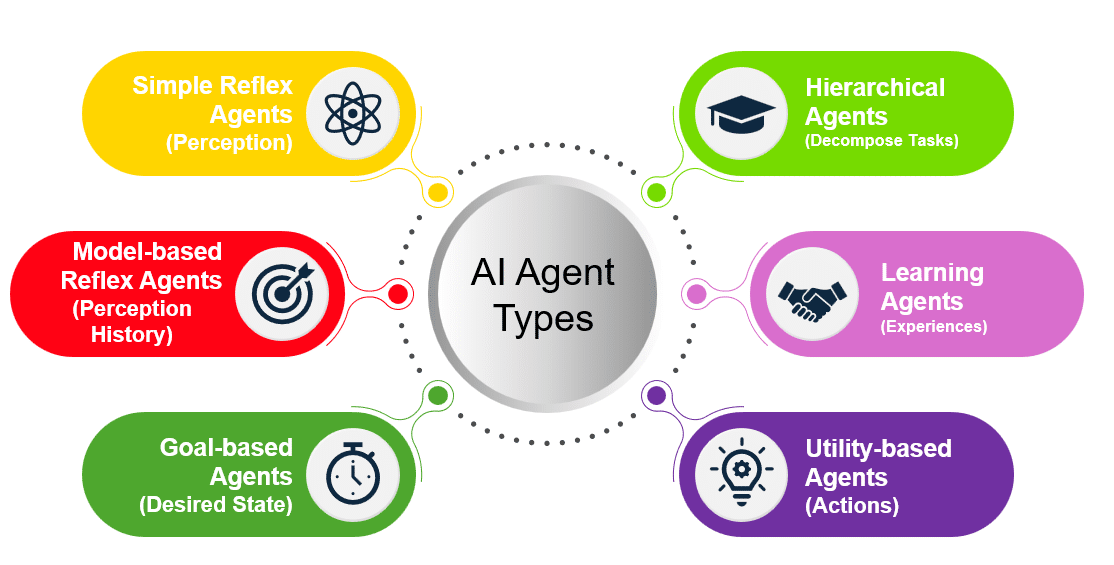
Types of AI Agents
- Simple Reflex Agents: React to current perceptions (e.g., automated hand sanitizer dispensers).
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: Handle partially observable environments (e.g., smart IV pumps).
- Goal-Based Agents: Aim to achieve specific goals (e.g., personalized treatment planning systems).
- Utility-Based Agents: Maximize expected utility (e.g., hospital resource allocation systems).
- Learning Agents: Improve performance over time (e.g., predictive analytics for patient monitoring).
- Hierarchical Agents: Break tasks into subtasks (e.g., hospital workflow management systems).
Business Adoption of AI Agents
Organizations must follow critical steps to integrate AI agents successfully:
- Governance: Establish frameworks for data privacy, security, and ethical use.
- Identify Use Cases: Focus on areas like customer service, predictive analytics, and automation.
- Change Management: Help teams adapt to AI-driven workflows.
- Infrastructure: Ensure IT systems can support AI computational demands.
- Upskilling: Train employees to work with AI agents.
Related News
Beginner-Friendly AI Agent Projects to Learn and Build
Explore five practical AI agent projects for beginners, covering scheduling, coding, content creation, research, and search functionalities.
Claude Sonnet 4 5 Advances AI Agents Toward OS Like Capabilities
Anthropic's Claude Sonnet 4.5 coding model demonstrates how AI agents could evolve into dynamic operating systems, raising questions about future app development and security.
About the Author

Dr. Emily Wang
AI Product Strategy Expert
Former Google AI Product Manager with 10 years of experience in AI product development and strategy formulation. Led multiple successful AI products from 0 to 1 development process, now provides product strategy consulting for AI startups while writing AI product analysis articles for various tech media outlets.